Windows 11 has been out for a while, and many users are considering upgrading. If your computer meets the hardware requirements, the installation process is straightforward. However, if your computer is incompatible, there are still ways to bypass the restrictions. In this blog, we’ll help you easily upgrade to Windows 11, whether your PC is compatible or not, starting from guiding you on how to download and install Windows 11, to presenting solutions for incompatible devices.
Check Your PC’s Compatibility with Windows 11
Before upgrading, the first step is to check if your PC meets the minimum system requirements for Windows 11. Microsoft has set the following standards:
- Processor: 1 GHz or faster, with at least two cores on a compatible 64-bit processor.
- Memory: 4 GB or larger.
- Storage: 64 GB or larger storage device.
- System Firmware: UEFI, capable of Secure Boot.
- TPM: Version 2.0.
- Graphics Card: DirectX 12 compatible with WDDM 2.0 driver.
- Display: >9″, HD resolution (720p).
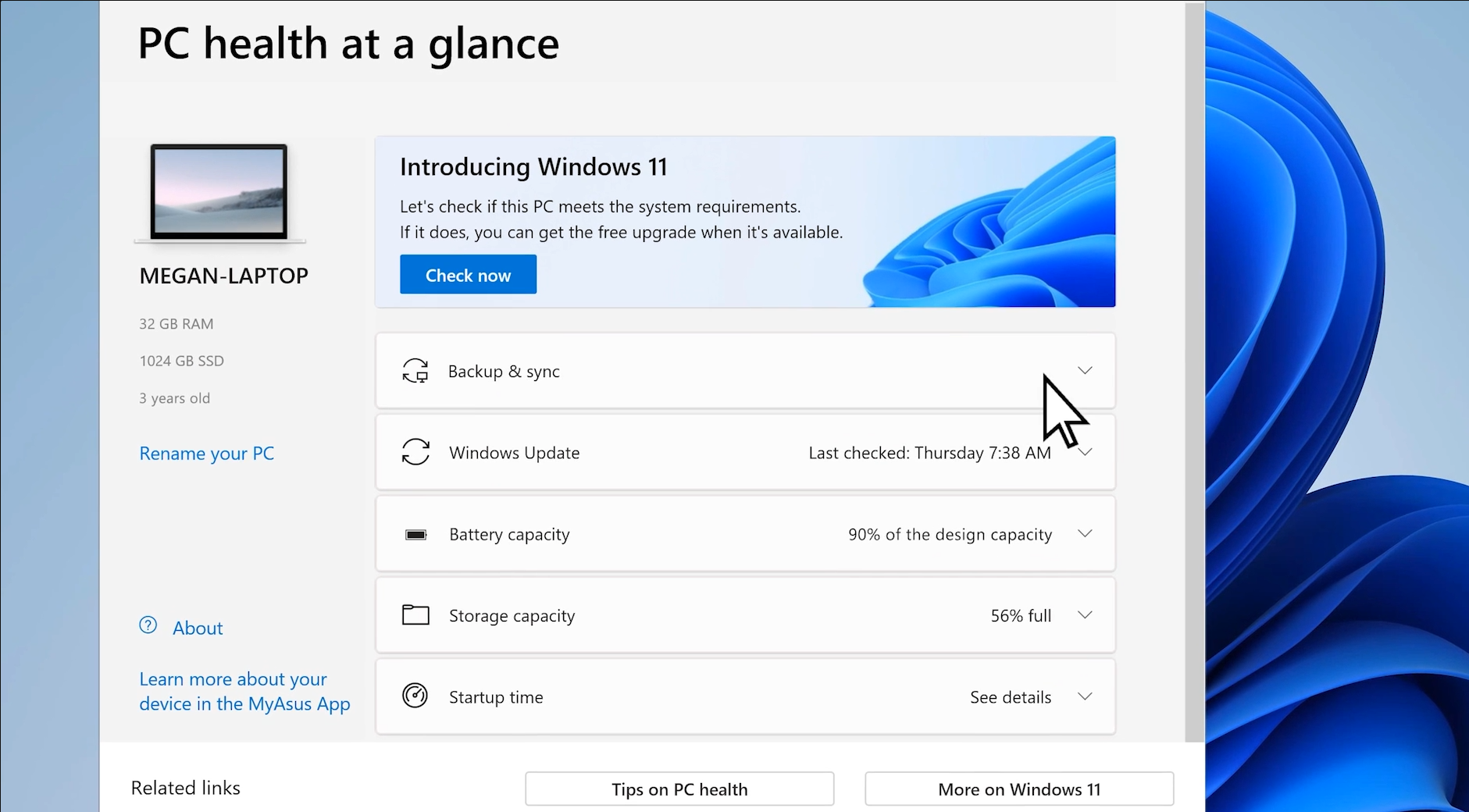
How to Check Compatibility
You can easily verify whether your PC is compatible using Microsoft’s PC Health Check tool, and check the Windows release information status for known issues that may affect your device.
Tip: If your device passes the compatibility check, continue to the next steps for installation. If not, don’t worry—we’ll discuss how to bypass hardware restrictions later in the blog.
How to Install Windows 11 on Compatible PCs
If your PC passes the compatibility check, the installation process will be straightforward. There are three methods to install Windows 11:
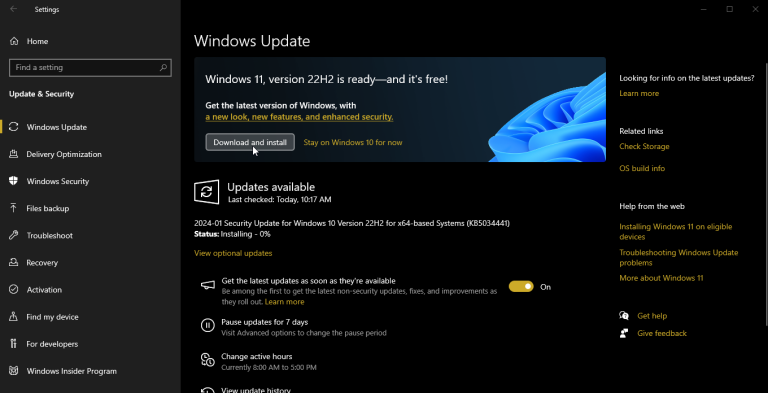
Method 1: Upgrade via Windows Update
The simplest way to upgrade to Windows 11 is through Windows Update. Follow these steps:
- Open Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates.
- If your PC is eligible, you will see the option to download and install Windows 11.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
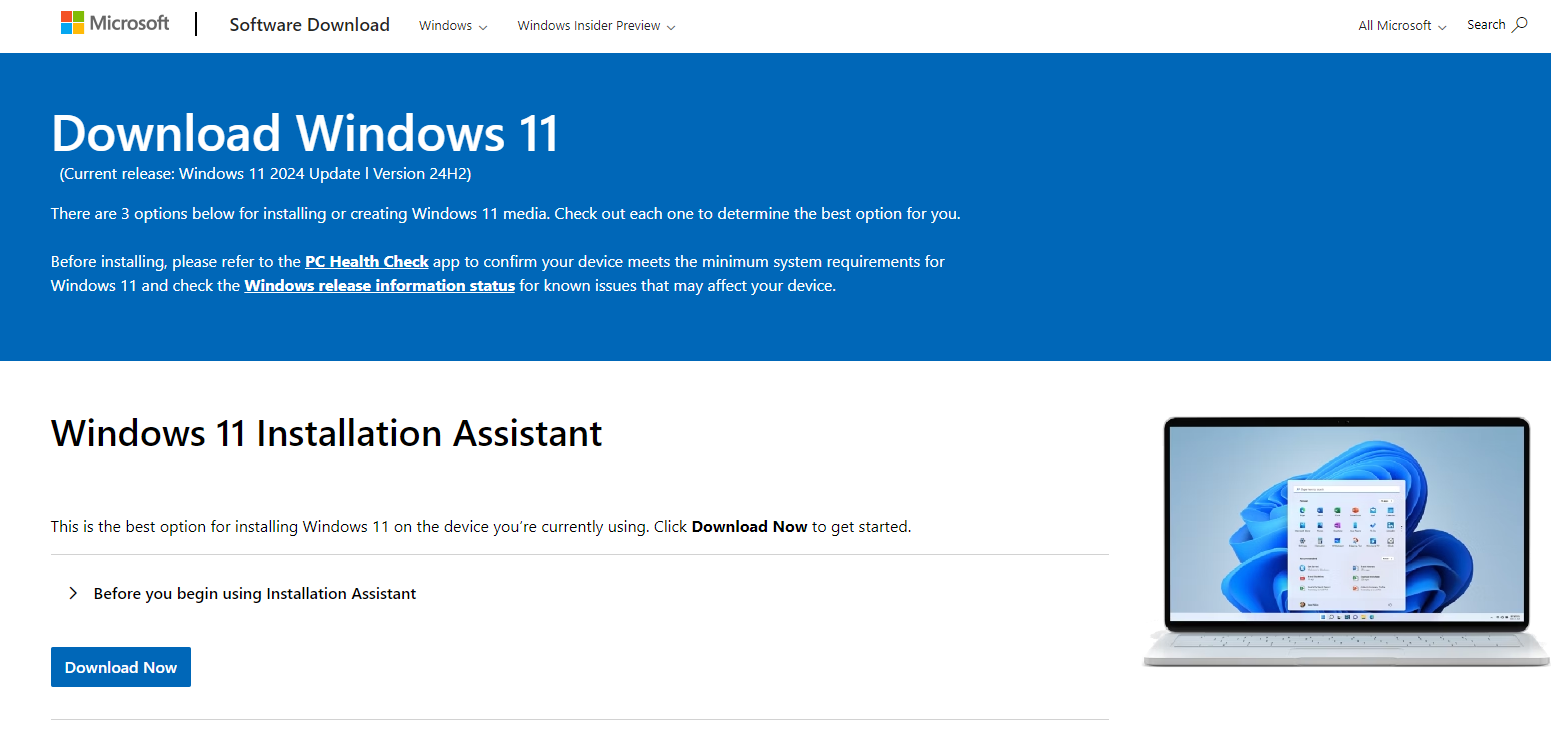
Method 2: Use the Windows Installation Assistant
If Windows Update doesn’t prompt the upgrade, you can use Microsoft’s Windows Installation Assistant:
- Go to the Windows 11 download page.
- Click Download Now under the Windows Installation Assistant section.
Run the file and follow the instructions to upgrade your PC to Windows 11.
Method 3: Create Windows 11 Installation Media
If you want to do a clean installation, upgrade multiple computers, work with unsupported devices, or install Windows 11 without an existing operating system, you can download the Media Creation Tool to make a bootable USB drive or DVD.
On the Windows 11 software download page, select Download Now under the Create Windows 11 Installation Media, then run the downloaded MediaCreationTool.exe file, accept the license terms, and follow the instructions to install Windows 11. You can choose to copy the installation files to a USB drive or generate an ISO file and burn it to a disk.
What If Your PC Is Not Compatible?
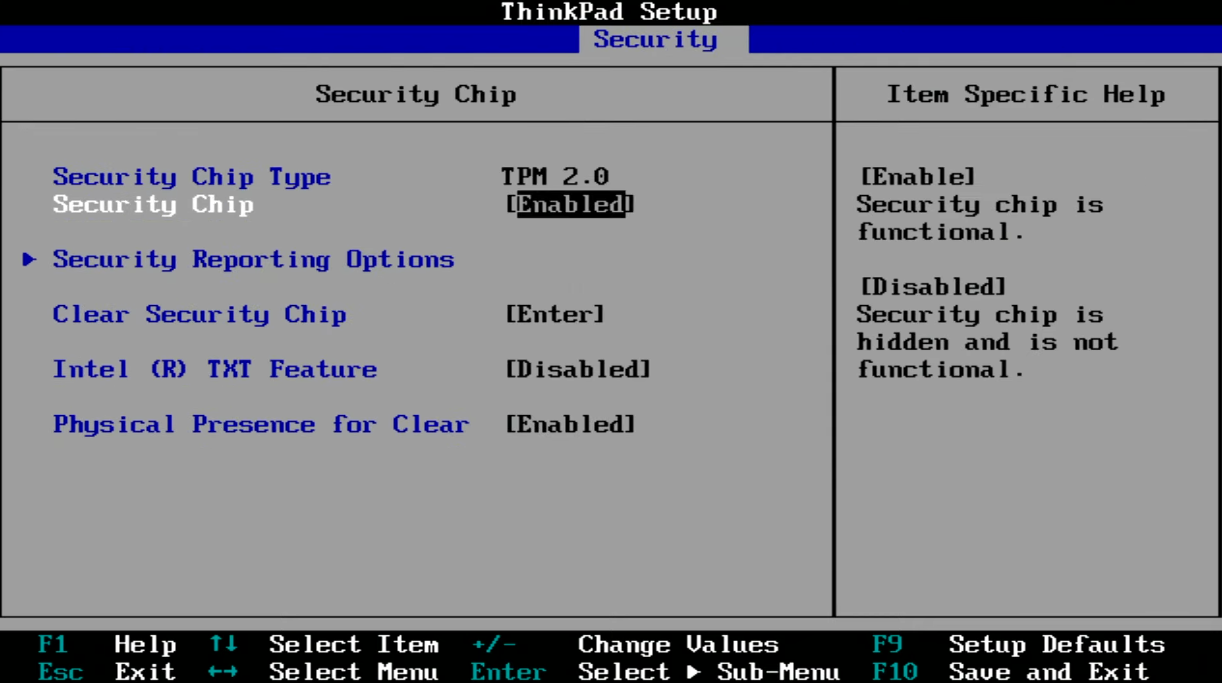
Some older PCs may not meet Windows 11’s strict system requirements, such as lacking features like TPM 2.0 or Secure Boot, which means they are considered “incompatible.” But don’t give up just yet! Many modern PCs have these features, but they might be disabled by default. You can resolve this by enabling them in your BIOS settings:
Enable TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot:
- Access the BIOS: Restart your PC and press the BIOS key (usually F2, F10, Delete, or Esc) during startup.
- Enable TPM: Look for “Security” or “Advanced” settings, find TPM, and enable it.
Enable Secure Boot: In the Boot section of your BIOS, make sure Secure Boot is turned on.
Risk Warning: Bypassing hardware requirements may compromise your system’s performance and security. Be sure to back up all your data and proceed with caution. After enabling these features, try running the Windows 11 installation again. Most PCs should pass the compatibility check once these settings are adjusted.
What If Your PC Is Unsupported?
If your PC has an older processor or is missing certain hardware, it may fall under the “unsupported” category. This means you won’t meet Windows 11’s official requirements, but you can still create a bootable USB drive or use an ISO file to bypass hardware checks and install Windows 11. However, be aware that unsupported PCs may not receive future updates or official support from Microsoft.
Bypass the Installation Restrictions: Manual Installation for Unsupported PCs
Here’s a quick overview of how to manually install on unsupported PCs:
- Download the Windows 11 ISO from the Microsoft website.
- Use the Media Creation Tool to create a bootable USB drive or DVD.
- During the installation process, modify the registry to bypass the TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot checks.
-
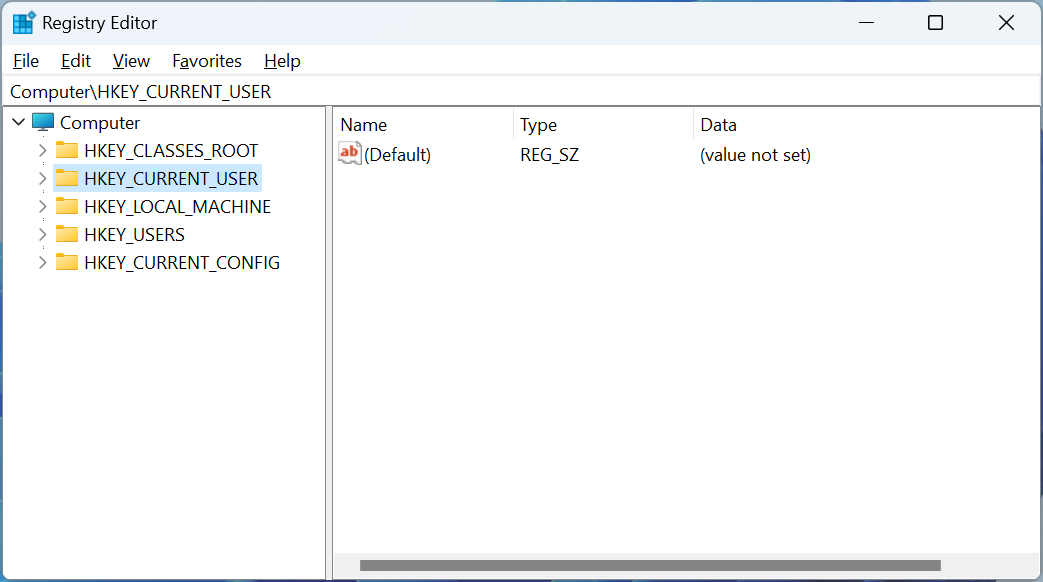
- Open the Registry Editor by pressing Win + R, typing regedit, and hitting Enter.
- Navigate to this path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Setup\MoSetup
- Right-click the blank area on the right side and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value. Name it AllowUpgradesWithUnsupportedTPMOrCPU, and set the value to 1.
- Save and exit the Registry Editor, then restart your PC. Afterward, you should be able to install Windows 11.
Risk Warning: Although this method lets you run Windows 11, there might be limitations in performance and security.
Completing the Windows 11 Upgrade
Whether your computer meets the system requirements for Windows 11 or not, the above steps will help you successfully upgrade to Windows 11, then follow the setup prompts to configure basic information such as network connections and accounts. Remember to check for system updates regularly after the upgrade to ensure you have the best security and performance. If you experience any problems or think that Windows 11 is not for you, you can roll back to Windows 10 using the system’s recovery option.
We hope this guide has provided valuable assistance in your upgrade journey! Have fun with Windows 11!